move readme to base directory
This commit is contained in:
parent
17426f8481
commit
b3b96014d0
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,141 @@
|
|||
# keyplus mini beta
|
||||
|
||||
## Errata rev2
|
||||
|
||||
The SS and MO pins are mislabeled. The SS pin should be MO, and the MO pin
|
||||
should be SS.
|
||||
|
||||
## Wiring
|
||||
|
||||
### Wiring key matrix
|
||||
|
||||
The key matrix should be wired to the ROW and COL pins on the PCB. Wiring of the
|
||||
ROW and COL and column pins should start from the lowest number pin (i.e. `ROW0`
|
||||
and `COL0`) and work up in consecutive order. The diodes in the key matrix should
|
||||
point from the COL to ROW pins (other scan modes not implemented yet).
|
||||
|
||||
The `COL15, COL14, COL13, COL12` pins (underlined on the PCB) may also be used
|
||||
as `ROW` pins. They map to the following row pins:
|
||||
|
||||
* ROW6: COL15
|
||||
* ROW7: COL14
|
||||
* ROW8: COL13
|
||||
* ROW9: COL12
|
||||
|
||||
Thus it is possible to have up to 120 keys connected using a 10x12 matrix.
|
||||
|
||||
### Wired split with I2C
|
||||
|
||||
To connect to boards with I2C for wired split, connect the 5V, SDA, SCL, and
|
||||
GND pins between devices. You can connect several devices in this manner, they
|
||||
just need to share 5V, SDA, SCL and GND pins.
|
||||
|
||||
I would recommend **NOT** using TRRS connectors for wired split. While connecting and
|
||||
disconnecting the device the contacts inside the TRRS cable can short to one
|
||||
another. Instead I would recommend using micro USB ports, or another
|
||||
connector that doesn't short it's contacts when it is plugged/unplugged. Then
|
||||
you will be able to take advantage of the wireless/wired hot plugging
|
||||
functionality without worrying about damaging the hardware. You can find
|
||||
male-to-male micro USB cables online with a bit of searching.
|
||||
|
||||
### Wireless with nRF24L01+
|
||||
|
||||
To use wireless mode, you will need a battery and a nRF24L01+ module. The
|
||||
battery should be 3V. Some options for the battery are 1xCR2032, 2xAA/AAA, or
|
||||
1xAA/AAA with a boost converter. Note the keyplus mini controller does not
|
||||
support any sort of charging of the batteries. When there is no USB connecting
|
||||
the device will run off battery power. When the USB is plugged in, it will
|
||||
automatically switch to run off USB power. To connect the battery connect:
|
||||
|
||||
* BAT -> positive battery terminal
|
||||
* GND -> negative battery terminal
|
||||
|
||||
To connect an nRF24L01+ module you will need to connect these pins:
|
||||
|
||||
* xmega -> nRF24L01+
|
||||
* R0 -> CE
|
||||
* R1 -> IRQ
|
||||
* MO -> MO / MOSI (Note: rev2 PCB use SS instead)
|
||||
* MI -> MI / MISO
|
||||
* SS -> SS / CSN (Note: rev2 PCB use MO instead)
|
||||
* SCK -> SCK
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Note: currently the IRQ pin is not used in the code, but I'll add code to take advantage of it soon.
|
||||
|
||||
### PCB schematic for rev 2
|
||||
|
||||
[Schematic for keyplus mini](https://rawgit.com/ahtn/keyboard_pcb/bb20b354216aa1858254db9946aa67aa8df67bfd/keyplus_mini/rev2/keyplus_mini.pdf)
|
||||
|
||||
### Mechanical information for rev 2
|
||||
|
||||
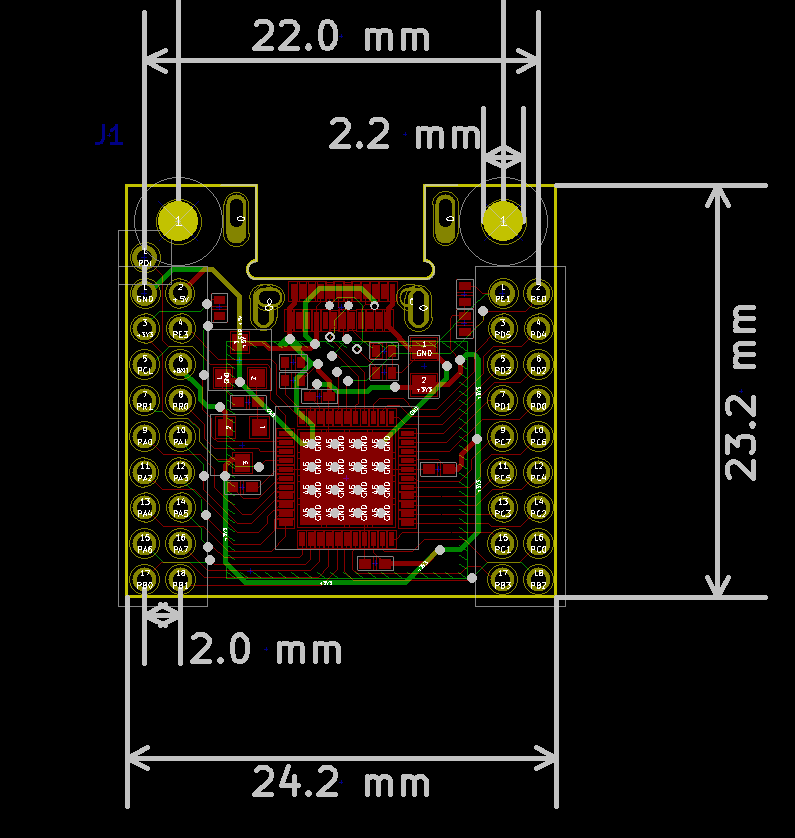
|
||||
|
||||
## Layout file format and programming
|
||||
|
||||
TODO
|
||||
|
||||
For [prebuilt versions of the loader and firmware](https://github.com/ahtn/keyplus/releases).
|
||||
|
||||
For the mean time, refer to the
|
||||
[example layouts](https://github.com/ahtn/keyplus/tree/master/layouts), and the
|
||||
[list of available keycodes](https://github.com/ahtn/keyplus/blob/master/host-software/layout/mapped_keycodes.py#L8).
|
||||
|
||||
## Current firmware limitations
|
||||
|
||||
Firmware is still in beta and several features are not completely
|
||||
finished yet. Some prominent ones:
|
||||
|
||||
* Macro and hold keycodes can't be used in the layout config file yet.
|
||||
* No LED support yet (including indicators)
|
||||
* Pairing unifying mouse is not exposed to devices yet
|
||||
|
||||
## Testing key matrix
|
||||
|
||||
The firmware supports a mode where it will pass the raw keyboard matrix data to
|
||||
the PC. This can be used to check the row and column pairs in your key matrix.
|
||||
Currently, this can only be used on the command line using a python script
|
||||
[`keyplus/host-software/keyplus_cli.py`](https://github.com/ahtn/keyplus/blob/master/host-software/keyplus_cli.py).
|
||||
|
||||
To use the keyboard matrix passthrough mode, run `./keyplus_cli.py passthrough`
|
||||
and you should see output like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$$ ./keyplus_cli.py passthrough
|
||||
r3c5
|
||||
|
||||
r3c0
|
||||
|
||||
r1c0
|
||||
|
||||
r0c1
|
||||
r0c1 r1c1
|
||||
r1c1
|
||||
r1c1 r3c3
|
||||
r3c3
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Where each line shows which keys in the matrix are currently being pressed.
|
||||
Note only devices directly connected by USB will report key presses using
|
||||
passthrough mode.
|
||||
|
||||
## xusb bootloader
|
||||
|
||||
The bootloader installed on the ATxmega is the [xusb bootloader](https://github.com/ahtn/xusb-boot).
|
||||
To enter bootloader mode press the reset button (or short the RST and GND
|
||||
contacts) once when the USB cable is plugged in. The device will remain in
|
||||
bootloader mode until it is programmed, or until the reset button is pressed a
|
||||
second time. For a more detailed explanation of the bootloader, [see
|
||||
here](https://github.com/ahtn/xusb-boot#ways-to-enter-the-bootloader).
|
||||
|
||||
The lock bits on the ATxmega have been set to disable reading from flash by an
|
||||
external programmer. This is done to protect the encryption keys that are
|
||||
stored in flash. Also, for security reasons the bootloader will wipe SRAM on
|
||||
power up.
|
||||
|
||||
## Trouble shooting
|
||||
|
||||
* Make sure that the battery contacts have a firm connection. I've had issues
|
||||
sometimes with my homemade CR2032 holders where vibrations from typing would
|
||||
cause the contacts to be unreliable.
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,141 +1,6 @@
|
|||
# keyplus mini beta
|
||||
# keyplus mini beta rev2
|
||||
|
||||
## Errata rev2
|
||||
|
||||
The SS and MO pins are mislabeled. The SS pin should be MO, and the MO pin
|
||||
* The SS and MO pins are mislabeled. The SS pin should be MO, and the MO pin
|
||||
should be SS.
|
||||
|
||||
## Wiring
|
||||
|
||||
### Wiring key matrix
|
||||
|
||||
The key matrix should be wired to the ROW and COL pins on the PCB. Wiring of the
|
||||
ROW and COL and column pins should start from the lowest number pin (i.e. `ROW0`
|
||||
and `COL0`) and work up in consecutive order. The diodes in the key matrix should
|
||||
point from the COL to ROW pins (other scan modes not implemented yet).
|
||||
|
||||
The `COL15, COL14, COL13, COL12` pins (underlined on the PCB) may also be used
|
||||
as `ROW` pins. They map to the following row pins:
|
||||
|
||||
* ROW6: COL15
|
||||
* ROW7: COL14
|
||||
* ROW8: COL13
|
||||
* ROW9: COL12
|
||||
|
||||
Thus it is possible to have up to 120 keys connected using a 10x12 matrix.
|
||||
|
||||
### Wired split with I2C
|
||||
|
||||
To connect to boards with I2C for wired split, connect the 5V, SDA, SCL, and
|
||||
GND pins between devices. You can connect several devices in this manner, they
|
||||
just need to share 5V, SDA, SCL and GND pins.
|
||||
|
||||
I would recommend **NOT** using TRRS connectors for wired split. While connecting and
|
||||
disconnecting the device the contacts inside the TRRS cable can short to one
|
||||
another. Instead I would recommend using micro USB ports, or another
|
||||
connector that doesn't short it's contacts when it is plugged/unplugged. Then
|
||||
you will be able to take advantage of the wireless/wired hot plugging
|
||||
functionality without worrying about damaging the hardware. You can find
|
||||
male-to-male micro USB cables online with a bit of searching.
|
||||
|
||||
### Wireless with nRF24L01+
|
||||
|
||||
To use wireless mode, you will need a battery and a nRF24L01+ module. The
|
||||
battery should be 3V. Some options for the battery are 1xCR2032, 2xAA/AAA, or
|
||||
1xAA/AAA with a boost converter. Note the keyplus mini controller does not
|
||||
support any sort of charging of the batteries. When there is no USB connecting
|
||||
the device will run off battery power. When the USB is plugged in, it will
|
||||
automatically switch to run off USB power. To connect the battery connect:
|
||||
|
||||
* BAT -> positive battery terminal
|
||||
* GND -> negative battery terminal
|
||||
|
||||
To connect an nRF24L01+ module you will need to connect these pins:
|
||||
|
||||
* xmega -> nRF24L01+
|
||||
* R0 -> CE
|
||||
* R1 -> IRQ
|
||||
* MO -> MO / MOSI (Note: rev2 PCB use SS instead)
|
||||
* MI -> MI / MISO
|
||||
* SS -> SS / CSN (Note: rev2 PCB use MO instead)
|
||||
* SCK -> SCK
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Note: currently the IRQ pin is not used in the code, but I'll add code to take advantage of it soon.
|
||||
|
||||
### PCB schematic for rev 2
|
||||
|
||||
[Schematic for keyplus mini](https://rawgit.com/ahtn/keyboard_pcb/bb20b354216aa1858254db9946aa67aa8df67bfd/keyplus_mini/rev2/keyplus_mini.pdf)
|
||||
|
||||
### Mechanical information for rev 2
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Layout file format and programming
|
||||
|
||||
TODO
|
||||
|
||||
For [prebuilt versions of the loader and firmware](https://github.com/ahtn/keyplus/releases).
|
||||
|
||||
For the mean time, refer to the
|
||||
[example layouts](https://github.com/ahtn/keyplus/tree/master/layouts), and the
|
||||
[list of available keycodes](https://github.com/ahtn/keyplus/blob/master/host-software/layout/mapped_keycodes.py#L8).
|
||||
|
||||
## Current firmware limitations
|
||||
|
||||
Firmware is still in beta and several features are not completely
|
||||
finished yet. Some prominent ones:
|
||||
|
||||
* Macro and hold keycodes can't be used in the layout config file yet.
|
||||
* No LED support yet (including indicators)
|
||||
* Pairing unifying mouse is not exposed to devices yet
|
||||
|
||||
## Testing key matrix
|
||||
|
||||
The firmware supports a mode where it will pass the raw keyboard matrix data to
|
||||
the PC. This can be used to check the row and column pairs in your key matrix.
|
||||
Currently, this can only be used on the command line using a python script
|
||||
[`keyplus/host-software/keyplus_cli.py`](https://github.com/ahtn/keyplus/blob/master/host-software/keyplus_cli.py).
|
||||
|
||||
To use the keyboard matrix passthrough mode, run `./keyplus_cli.py passthrough`
|
||||
and you should see output like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$$ ./keyplus_cli.py passthrough
|
||||
r3c5
|
||||
|
||||
r3c0
|
||||
|
||||
r1c0
|
||||
|
||||
r0c1
|
||||
r0c1 r1c1
|
||||
r1c1
|
||||
r1c1 r3c3
|
||||
r3c3
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Where each line shows which keys in the matrix are currently being pressed.
|
||||
Note only devices directly connected by USB will report key presses using
|
||||
passthrough mode.
|
||||
|
||||
## xusb bootloader
|
||||
|
||||
The bootloader installed on the ATxmega is the [xusb bootloader](https://github.com/ahtn/xusb-boot).
|
||||
To enter bootloader mode press the reset button (or short the RST and GND
|
||||
contacts) once when the USB cable is plugged in. The device will remain in
|
||||
bootloader mode until it is programmed, or until the reset button is pressed a
|
||||
second time. For a more detailed explanation of the bootloader, [see
|
||||
here](https://github.com/ahtn/xusb-boot#ways-to-enter-the-bootloader).
|
||||
|
||||
The lock bits on the ATxmega have been set to disable reading from flash by an
|
||||
external programmer. This is done to protect the encryption keys that are
|
||||
stored in flash. Also, for security reasons the bootloader will wipe SRAM on
|
||||
power up.
|
||||
|
||||
## Trouble shooting
|
||||
|
||||
* Make sure that the battery contacts have a firm connection. I've had issues
|
||||
sometimes with my homemade CR2032 holders where vibrations from typing would
|
||||
cause the contacts to be unreliable.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue